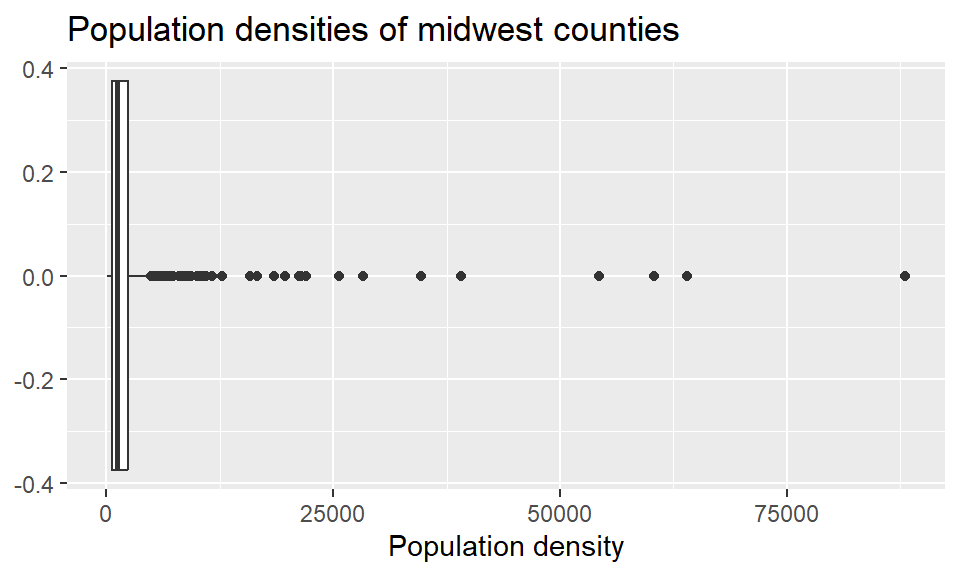
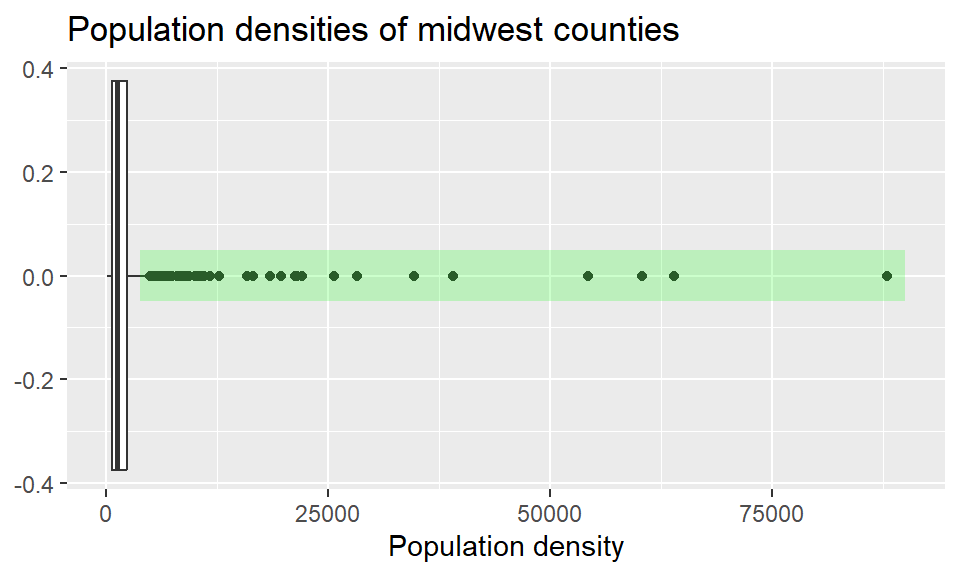
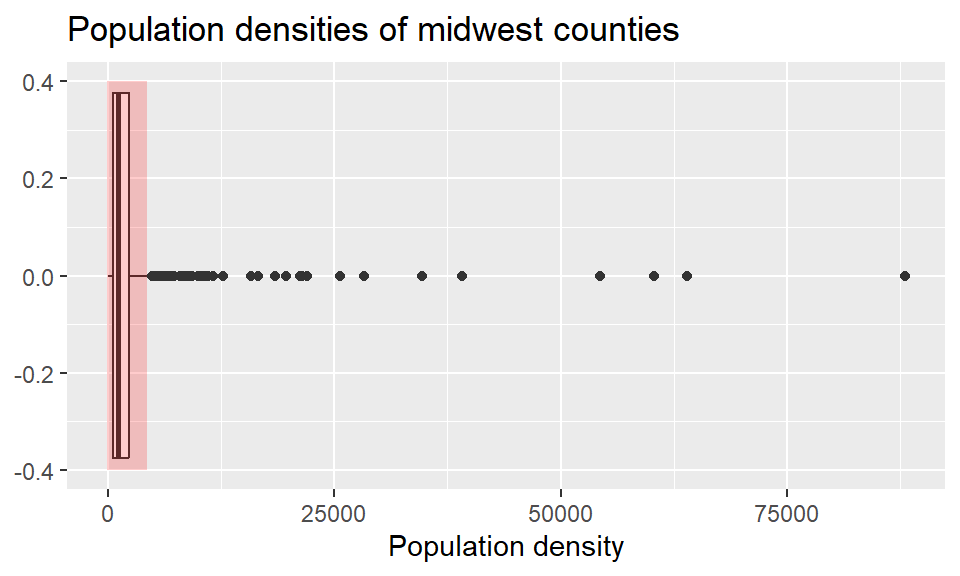
Loading required package: ggplot2── Attaching core tidyverse packages ────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.5
✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
✔ lubridate 1.9.3 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
✔ purrr 1.0.2 ✔ tidyr 1.3.1
── Conflicts ──────────────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors